Electric mobility has become mainstream, and the EV charger is central to this change. Whether you want to set up a public charging hub, enhance a commercial property, or provide home charging, understanding the equipment is essential for smooth operation.
Understanding the Main Types of EV Charger
Choosing the right [EV charger] starts with recognizing the two main technologies in today’s market.
AC Chargers – Reliable Workhorses for Everyday Use
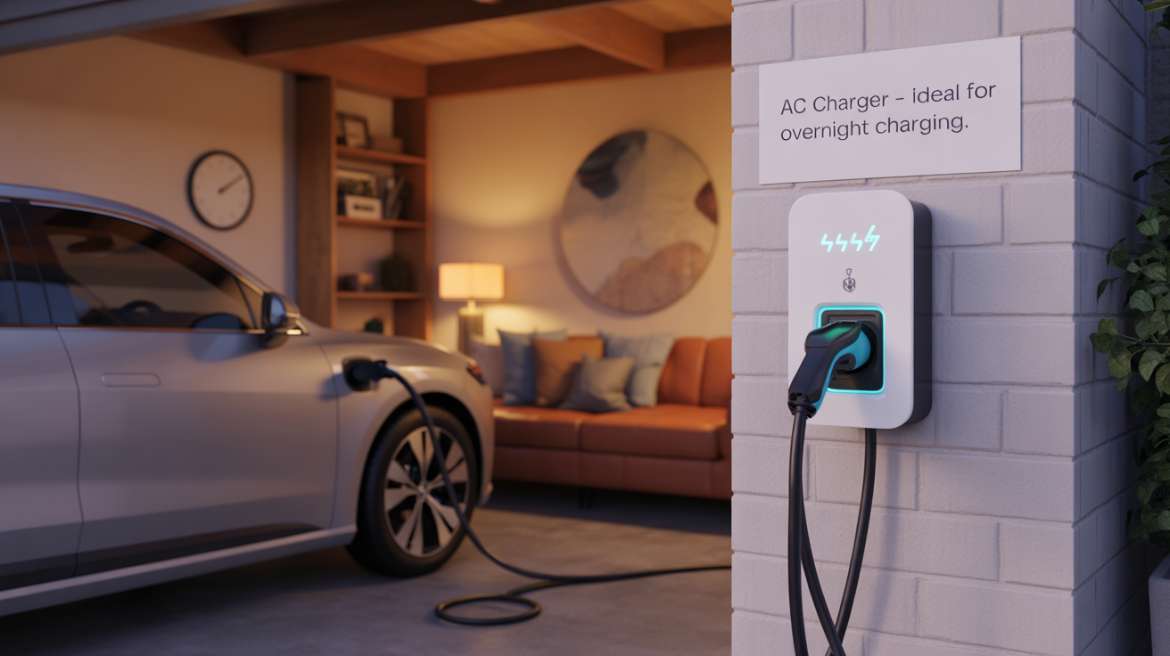

An AC charger provides alternating current to the vehicle’s on-board charger, which converts it to DC for battery storage. Since the vehicle handles the conversion, charging speed is limited to the on-board unit’s rating. This results in a “slow” charge cycle of about six to eight hours, ideal for long parking times—like in office buildings, hotels, residential garages, or retail parks. AC chargers range from 3.3 kW to 22 kW, making them a simple and cost-effective option for widespread charging.
Highlights
– Compact size and low installation costs
– Ideal for overnight or workday charging
– Power output from 3.3 kW to 22 kW (Level 1 and Level 2)
– Full charge typically takes 6–8 hours
DC Chargers – High-Capacity Solutions for Rapid Turnover

A DC charger delivers direct current straight to the battery, bypassing the vehicle’s conversion stage. With power levels from 25 kW to 240 kW, a DC fast charger can recharge most electric cars in under an hour. Although the initial cost is higher, the faster charging times make DC chargers suitable for public locations, motorway services, fleet depots, and busy urban areas.
Highlights
– Charges an average EV in as little as 30–45 minutes
– Power levels from 25 kW to 240 kW
– Designed for revenue-generating commercial sites and high-mileage fleets
– Supports larger vehicles like e-buses with appropriate connectors
Picking AC or DC for a Specific Site

If your site has long dwell times and limited grid capacity, an AC EV charger keeps costs low while meeting driver needs. For locations requiring quick turnover—like taxi ranks or logistics depots—investing in a high-capacity DC solution is sensible. Many operators use a mix of both types to accommodate various situations.
Essential Features that Differentiate Today’s EV Charger
Modern EV chargers offer features that enhance safety, efficiency, and profitability.
Certified Safety You Can Trust
Manufacturers like Delta ensure compliance with global standards through certifications such as UL, IEC, CHeMO, CQC, CNS, and ARAI/ICAT. These certifications protect hardware from electrical faults, reassure insurers, and keep drivers safe.
Intelligent Metering and Adjustable Power
Advanced models include digital energy meters that track every kilowatt, allowing for accurate billing and energy management. Adjustable power settings let you reduce output during grid constraints or off-peak hours, helping manage costs.
Built-in Communication for Seamless Integration
Modern EV chargers connect to cloud platforms via Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and GSM modules. This connectivity enables over-the-air updates, remote diagnostics, and real-time session data, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Rugged, Weatherproof Construction
Whether you install a Bharat AC-001 indoors or a 120 kW DC charger outdoors, weather protection is crucial. Quality chargers are sealed against dust, rain, and splashes, ensuring reliable service year-round.
User Authentication and Secure Access
RFID card readers and mobile app pairing restrict charging to authorized users, support subscription models, and prevent energy theft. For example, Servotech’s 3.3 kW wall box supports GSM, Wi-Fi, and RFID in one unit.
EV Charging Networks: How the Pieces Come Together
Single charging stations are useful, but a network offers greater scaling potential.
Wide Coverage Brings Confidence
Tata Power EZ Charge operates over 5,500 public points, 120,000 home chargers, and more than 1,200 bus connectors across 620+ cities. This extensive network reassures drivers that charging is always nearby, encouraging EV adoption and increasing foot traffic to businesses.
Supporting Cars, Vans, and Buses
A mature network combines AC and DC equipment, ensuring that commuter cars, last-mile vans, and full-size buses can all find suitable charging options. Delta’s range includes everything from compact AC wall units to megawatt-class depot chargers.
The Power of Apps and Smart Cards

Mobile apps help users locate available chargers, reserve slots, and pay upon arrival. Tap-and-go RFID cards, like the EZ CHARGE India card, offer a similar experience for those who prefer physical tokens. Both methods streamline revenue collection and reduce wait times.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Operators sometimes underestimate the demand for fast charging in retail or hospitality settings. Pairing a few AC sockets with at least one DC charger can satisfy drivers looking for a quick top-up while increasing turnover. Additionally, a user-friendly app is essential to keep charging bays busy.
Installation and Connectivity: Laying the Foundations
Installing an EV charger is easier than many newcomers think—if you follow best practices.
Simple, Standards-Based Interfaces

Today’s chargers support global plug formats like Type 2 AC and CCS-2 DC, allowing your site to accommodate all mainstream vehicles without adapters. Delta’s multi-protocol hardware exemplifies this approach, ensuring mixed-fleet compatibility.
Scalable Electrical Infrastructure
A single 7.4 kW home unit typically requires a standard single-phase supply. A public 120 kW DC charger will need three-phase power and possibly utility approval. Plan wiring routes, grounding, and load balancing early to avoid costly changes later.
Always-On Connectivity Keeps You in Control

Ethernet is the most reliable option for data transfer, but Wi-Fi and GSM offer quick solutions where cabling is difficult. Over-the-air software updates keep your EV charger compliant with evolving standards without needing a site visit.
Secure Access Protection
RFID authentication prevents unauthorized use, especially in open parking lots. Many operators combine RFID with CCTV and tamper alarms for added security.
Lessons from the Field
Delaying the choice between Level 1 and Level 2 AC units can lead to under-specification and frustrated drivers. Overlooking connectivity infrastructure can turn a smart charger into an offline, revenue-losing asset.
Practical Considerations for a Profitable Charging Operation
Successful charging businesses balance user needs, grid capacity, and financial return.
Matching Charger Type to Usage Profile
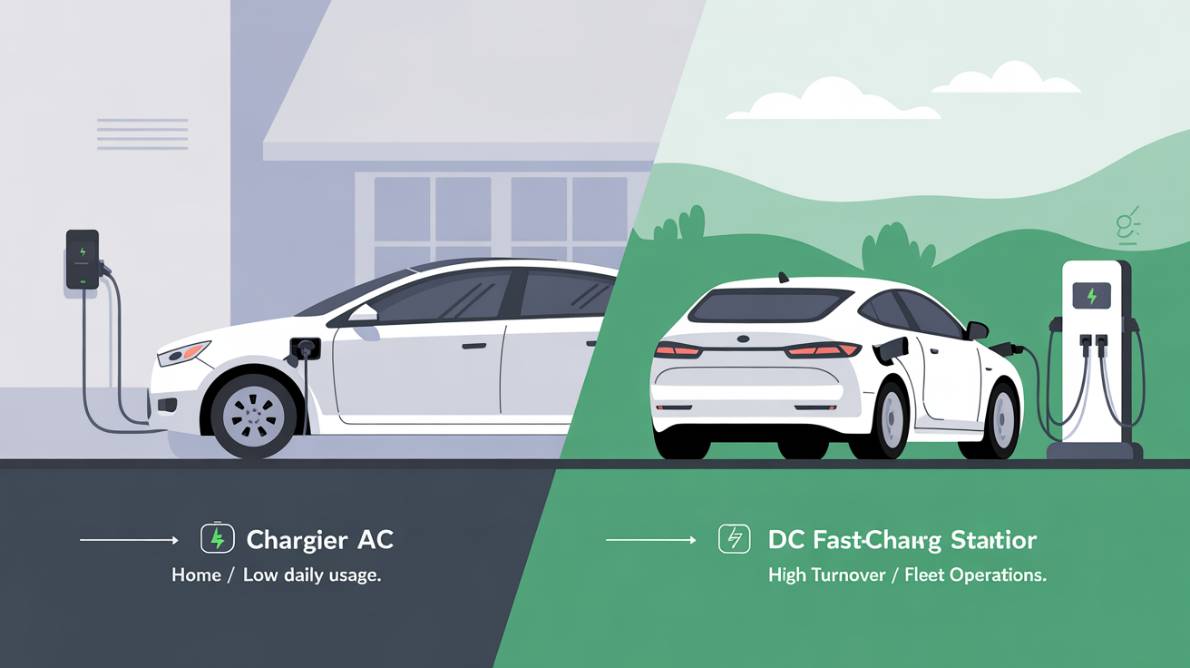
If your customers stay for hours—like while shopping—an AC EV charger is cost-effective. High-traffic sites that require frequent departures will benefit from at least one high-capacity DC charger. Mixed installations can cover both needs without overspending.
Managing Energy Costs
High-efficiency power electronics, like those in Delta’s latest range, minimize energy loss, lowering operational costs. Adjustable current settings allow you to reduce output when electricity prices rise, maintaining profit margins without sacrificing service.
Rolling Out a Network Swiftly

Servotech’s multi-socket AC solutions, including the Bharat AC-001, enable rapid deployment of three simultaneous charging points from one unit. Pairing these chargers with a cloud back-end allows you to open multiple locations in weeks instead of months.
Enabling Friction-Free Payments
Instant online payments through compliant apps or RFID streamline revenue collection. Lower transaction costs mean you keep more of each kilowatt sold, which adds up over thousands of sessions.
Compliance and Future-Proofing
Always check that your chosen EV charger has up-to-date safety and communication certifications. Over-the-air firmware updates will protect your investment and prevent costly equipment replacements.
Case in Point: Mixed-Site Deployment

A hospitality complex might install four 7 kW AC wall boxes in the guest parking area, a 50 kW DC charger at the entrance, and a Thunderplus-branded smart pedestal near the concierge desk for valet charging. This combination serves overnight guests, day visitors, and fast-charge emergencies, ultimately boosting revenue in rooms, dining, and transport.
If you want your EV charger to operate smoothly and efficiently, ThunderPlus offers a strong network and support for all your charging needs. Visit us at thunderplus.io to explore our franchise models and find the right solution for your EV charging station.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is an EV charger?
An EV charger supplies electrical energy to an electric vehicle’s battery. It manages power flow, safety interlocks, and communication with the car for a controlled, efficient charge.
Q2. How does an EV charger compare with a regular socket?
A dedicated EV charger includes protective circuits, coded connectors, and smart communication, allowing for higher power delivery and safer operation than a standard household plug.
Q3. Where can I find EV chargers near me?
Public networks like Tata Power EZ Charge list nearby stations in their mobile apps, showing real-time availability, connector types, and pricing before you head out.
Q4. How do I decide between Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging for my site?
Consider dwell time and turnover. Long-stay locations usually do well with Level 1 or Level 2 AC units, while high-traffic sites benefit from at least one DC fast charger for quick sessions.
Q5. Are AC chargers really cheaper to operate than DC units?
Yes. AC chargers are less expensive to buy and install, and they draw lower peak power, reducing demand charges. However, DC chargers can generate more revenue if users need quick top-ups.
**Q6. My charger shows a fault code after a storm—what should I


